 Problem C. 1765. (April 2023)
Problem C. 1765. (April 2023)
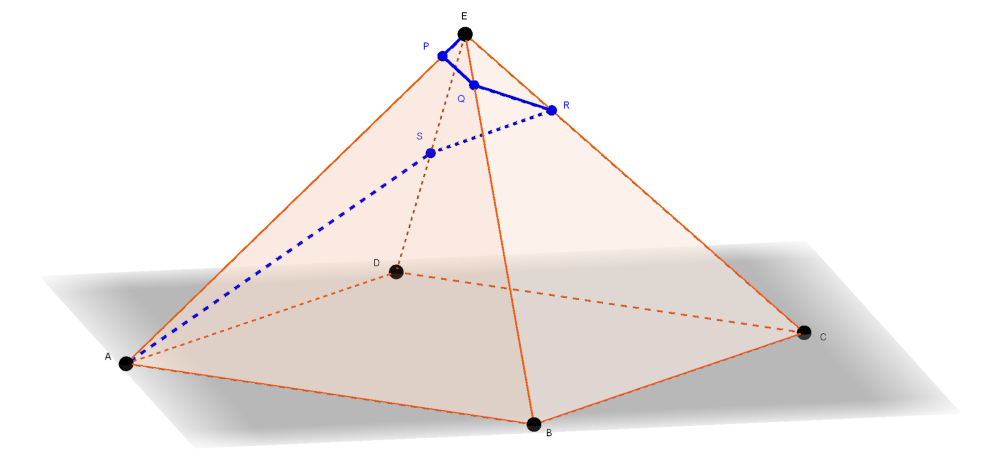
C. 1765. The base of a regular four-sided pyramid \(\displaystyle ABCDE\) is the square \(\displaystyle ABCD\), and each edge of the pyramid is \(\displaystyle 32\) units long. A snail starts at vertex \(\displaystyle E\) and crawls to vertex \(\displaystyle A\) as follows: first moves along edge \(\displaystyle EA\) to the point \(\displaystyle P\) for which \(\displaystyle EP=2\). Then continues to cross the face \(\displaystyle ABE\) and arrives at point \(\displaystyle Q\) of edge \(\displaystyle EB\), where \(\displaystyle EQ=4\). Then crosses the face \(\displaystyle BCE\) to reach that point \(\displaystyle R\) of edge \(\displaystyle EC\) for which \(\displaystyle ER=8\), and continues along face \(\displaystyle CDE\) to point \(\displaystyle S\) on edge \(\displaystyle ED\), with \(\displaystyle ES=16\). Finally, it crawls on the surface of face \(\displaystyle DAE\), from \(\displaystyle S\) to point \(\displaystyle A\). What is the minimum distance covered by the snail altogether?
Proposed by B. Bíró, Eger
(5 pont)
Deadline expired on May 10, 2023.
Sorry, the solution is available only in Hungarian. Google translation
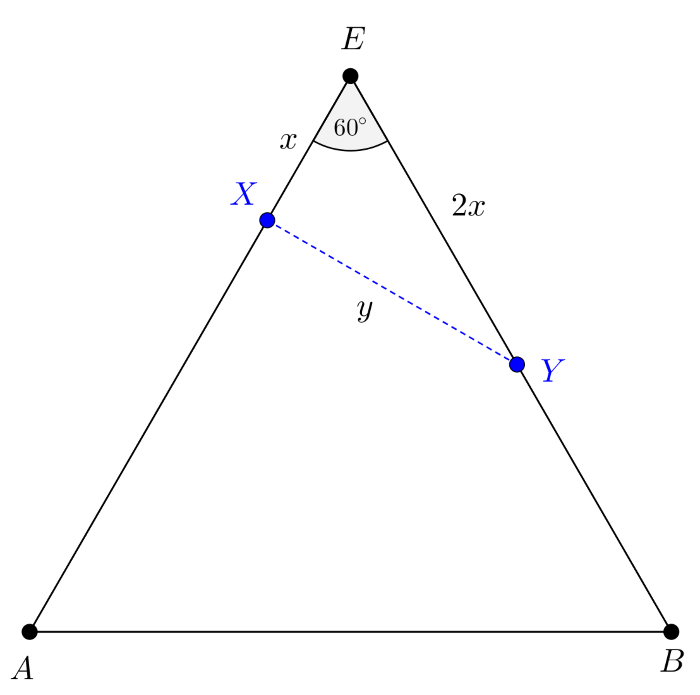
Megoldás. Válasszuk ki a gúla egyik lapján, például az \(\displaystyle ABE\) lapon az \(\displaystyle AE\) él egy tetszőleges \(\displaystyle X\) belső pontját, amelyre \(\displaystyle EX=x\) és a \(\displaystyle BE\) élen azt az \(\displaystyle Y\) pontot, amelyre \(\displaystyle EY=2x\), legyen továbbá \(\displaystyle XY=y\). Tekintsük az 1. ábrát.
1. ábra
Az \(\displaystyle EXY\) háromszögben felírjuk a koszinusztételt az \(\displaystyle y\) hosszúságú oldalra:
\(\displaystyle y^2=x^2+4x^2-4x^2\cdot \cos60^{\circ},\)
ahonnan \(\displaystyle \displaystyle{\cos60^{\circ}=\frac{1}{2}}\) ismeretében \(\displaystyle y^2=3x^2\), emiatt pedig
\(\displaystyle x^2+y^2=4x^2.\)
A kapott összefüggés a Pitagorasz-tétel megfordítása alapján azt jelenti, hogy az \(\displaystyle EXY\) az \(\displaystyle X\) pontban derékszögű háromszög, azaz \(\displaystyle XY\) merőleges az \(\displaystyle AE\) szakaszra.
Nyilvánvaló, hogy ha \(\displaystyle X\) az \(\displaystyle E\)-től az \(\displaystyle AE\) szakasz felénél (\(\displaystyle 16\) egységnél) kisebb távolságra van, akkor \(\displaystyle Y\) a \(\displaystyle BE\) szakasz belső pontja, ha pedig \(\displaystyle \displaystyle{EX=\frac{AE}{2}}\), akkor \(\displaystyle Y=B\).
Az \(\displaystyle X\) és \(\displaystyle Y\) pontok közötti legrövidebb távolság a két pontot összekötő egyenes szakasz.
A csiga tehát, amikor az \(\displaystyle ABE\) lapon az \(\displaystyle X\) pontból az \(\displaystyle Y\) pontba mászik, a feladat feltételei mellett akkor teszi meg a legrövidebb utat, ha az \(\displaystyle X\) pontból az \(\displaystyle AE\) élre merőleges irányban haladva az \(\displaystyle Y\) pontba jut, megtett útjának hossza
| \(\displaystyle (1)\) | \(\displaystyle XY=x\sqrt{3}.\) |
A feltétel miatt az \(\displaystyle ABE\) lapon \(\displaystyle x=EP=2\) és \(\displaystyle EQ=2x=4\), ezért (1) szerint a csiga úthossza ezen a lapon
| \(\displaystyle (2)\) | \(\displaystyle PQ=2\sqrt{3}.\) |
Mivel \(\displaystyle EQ=4, ER=8\) és \(\displaystyle ES=16\), ezért hasonlóan kapjuk, hogy a csiga a \(\displaystyle BCE\) lapon akkor teszi meg a legrövidebb utat, ha a \(\displaystyle Q\) pontból a \(\displaystyle BE\) szakaszra merőlegesen haladva jut az \(\displaystyle R\) pontba, a \(\displaystyle CDE\) lapon az \(\displaystyle R\) pontból a \(\displaystyle CE\)-re merőleges irányban haladva a \(\displaystyle DE\) él \(\displaystyle S\) pontjába érkezik, végül a \(\displaystyle DAE\) lapon az \(\displaystyle S\) pontból a \(\displaystyle DE\)-re merőlegesen haladva jut az \(\displaystyle AE\) él \(\displaystyle A\) pontjába. Ezekből (2)-höz hasonlóan adódik, hogy
| \(\displaystyle (3)\) | \(\displaystyle QR=4\sqrt{3}, \quad RS=8\sqrt{3}, \quad SA=16\sqrt{3}.\) |
2. ábra
A 2. ábrán látható \(\displaystyle EPQRSA\) térbeli töröttvonal hosszát (2) és (3) felhasználásával kapjuk:
\(\displaystyle EP+PQ+QR+RS+SA=2+30\sqrt{3}\approx 53,96.\)
A csiga tehát a gúla \(\displaystyle AE\) élén és a gúla lapjain összesen legalább \(\displaystyle 2+30\sqrt{3}\approx 53,96\) távolságegységnyi utat tesz meg.
Statistics:
107 students sent a solution. 5 points: 53 students. 4 points: 25 students. 3 points: 12 students. 2 points: 5 students. 0 point: 1 student. Unfair, not evaluated: 3 solutionss.
Problems in Mathematics of KöMaL, April 2023
