KöMaL Problems in Physics, December 2022
Please read the rules of the competition.
Show/hide problems of signs:
 |
Problems with sign 'M'Deadline expired on January 16, 2023. |
M. 418. Measure the rotational inertia of a ball (e.g. football, table tennis ball or tennis ball) by rolling it down a slope. Give the result also in units of \(\displaystyle mR^2\) (where \(\displaystyle R\) is the radius of the ball, \(\displaystyle m\) is its mass). Can the result be used to infer the thickness of the wall of the ball?
(6 pont)
 |
Problems with sign 'G'Deadline expired on January 16, 2023. |
G. 797. An inflated balloon is attached to the open end of a liquid-column manometer. The difference in the level of petroleum in the two arms of the manometer is 72 cm. How many mm would the difference in level be if the manometer contained mercury? What is the gauge pressure (excess pressure) in the balloon?
(3 pont)
solution (in Hungarian), statistics
G. 798. In a 100 m flat race, the competitors will start from a kneeling start. The figure shows the horizontal force applied to the front and rear sensors in the starting machine when an athlete weighing 70 kg starts. Estimate the speed at which the athlete leaves the starting machine.
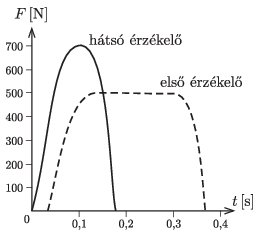
(3 pont)
solution (in Hungarian), statistics
G. 799. What is the minimum speed and maximum angle at which a body must be launched in order that it flies through a 100 metre long and 5 metre high straight tunnel?
The air drag is negligible.
(3 pont)
solution (in Hungarian), statistics
G. 800. An object is located at a certain distance from a converging lens, which forms the real, inverted image of the object of magnification \(\displaystyle N_1\). When the object is placed further from the lens, with a distance of \(\displaystyle d\) along the principal axis of the lens, the magnification becomes \(\displaystyle N_2\).
What is the focal length of the lens?
(4 pont)
 |
Problems with sign 'P'Deadline expired on January 16, 2023. |
P. 5445. An explosive projectile of mass \(\displaystyle M\) was fired at an angle of \(\displaystyle \alpha\) and at an initial speed of \(\displaystyle v_0\). At the top of its trajectory, the projectile exploded into two parts of masses \(\displaystyle m_1\) and \(\displaystyle m_2\), and the part with mass \(\displaystyle m_2\) started to fall freely at this moment.
\(\displaystyle a)\) How far apart will the two parts hit the ground?
\(\displaystyle b)\) What are the velocities of the two parts at their impact with the ground? (Determine both the speed and the direction of he velocity.)
(Data: \(\displaystyle M = 0.6\) kg, \(\displaystyle m_1 = 0.2\) kg, \(\displaystyle \alpha=60^\circ\), \(\displaystyle v_0 = 100\) m/s. Air drag is negligible.)
(4 pont)
solution (in Hungarian), statistics
P. 5446. Two students prepare for a stunt. At the same moment they both kick a football, that are at a certain distance \(\displaystyle d\) apart on a sports field, so that the balls meet in the air. One student kicks the ball at \(\displaystyle v_1=20\) m/s and the other at \(\displaystyle v_2=10\) m/s, but they can both decide on the direction of the initial velocity. What is the maximum initial distance \(\displaystyle d_{\max}\) between the two balls for the stunt to succeed?
(Air drag is negligible.)
(5 pont)
solution (in Hungarian), statistics
P. 5447. Three identical cylinders of radius 5 cm are made of ice and they are released without initial speed from the position shown in the figure. Friction is negligible everywhere.
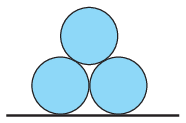
What is the acceleration at which the ice cylinders start moving?
(5 pont)
solution (in Hungarian), statistics
P. 5448. According to Edward, riding the bicycle in crosswind (wind which blows perpendicularly to the direction of the motion) is about as hard as to ride the bicycle when there is no wind. The crosswind pushes the bike only sideways, which doesn't slow you down. You just have to lean a little to go straight, and the headwind you're feeling is the same in both cases. Is Edward right?
(4 pont)
solution (in Hungarian), statistics
P. 5449. A 20 cm long copper rod with a cross section of 3 cm\(\displaystyle {}^2\) is surrounded by a good insulating sheath. The rod is held vertically and suspended at one end such that the other is in a glass containing melting ice; thus it is kept at a constant temperature of 0 \(\displaystyle {}^\circ\)C. To what temperature does the other end of the rod warms up when heated with a small 100 W filament coil? (The required constants can be found in tables or on the internet.)
(3 pont)
solution (in Hungarian), statistics
P. 5450. On the principal axis of a converging lens of focal length \(\displaystyle f=5\) cm, there are (point-like) fireflies, which begin to move towards each other at a speed of 2 cm/s. Initially one is 30 cm to the right and the other is 18 cm to the left of the lens. How much time elapses until their images overlap?
(4 pont)
solution (in Hungarian), statistics
P. 5451. The AC power supply for a garage is provided by a three-phase supply. A five-strand cable is used, with all five strands made of the same material and cross-section. One of the wires (green-yellow) is the protective conductor (ground), on which no current flows in the event of fault-free operation. The neutral conductor (blue) always has a potential of zero, and is practically always at ground potential. In the three phase conductors (brown, black, and grey) the potential is a sinusoidal function of time and varies such that the root-mean-square (rms) value is 230 V. The phase difference between the potentials of any two phase conductors is \(\displaystyle 120^\circ\). Resistors are connected between each phase conductor and the neutral conductor.
\(\displaystyle a)\) What is the rms value of the voltage between two different phase cables?
\(\displaystyle b)\) What is the rms value of the current in the neutral wire if the current in two phase conductors is 10 A, in each, but there is no current in the third phase conductor?
\(\displaystyle c)\) What is the rms current in the neutral wire if the current in each phase wire is 10 A?
\(\displaystyle d\)) What is the minimum and the maximum rms current in the neutral conductor if none of the rms currents in the phase conductors exceed 10 A?
(4 pont)
solution (in Hungarian), statistics
P. 5452. The initial mass of a photon rocket when it starts moving along a straight path is \(\displaystyle m_0\). Determine the speed of the rocket as a function of the instantaneous rest mass of the rocket.
(4 pont)
solution (in Hungarian), statistics
P. 5453. There is a point-like charge \(\displaystyle Q\) at a distance of \(\displaystyle d=0{.}5\) m from the centre of an uncharged metal sphere of radius \(\displaystyle r=0.2\) m. Determine the angle (with respect to the point charge) that is subtended by the points of the metal sphere with surface charge density equal to zero. (Numerical methods are also acceptable.)
(6 pont)
Upload your solutions above.
